DropBot: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „{{Projekt |projectname=DropBot |subcat=Gewerbe, Industrie |Images={{ProjektImages |projectimage=36.1.jpg }}{{ProjektImages |projectimage=36.2.jpg }}{{ProjektIm…“) |
K |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
{{Projekt | {{Projekt | ||
|projectname=DropBot | |projectname=DropBot | ||
| − | |subcat= | + | |subcat=Construction elevators |
|Images={{ProjektImages | |Images={{ProjektImages | ||
|projectimage=36.1.jpg | |projectimage=36.1.jpg | ||
Version vom 31. Januar 2019, 04:22 Uhr
|
|
DropBot Basic Data Category: Construction elevators URL (first publication): http://microfluidics.utoronto.ca/dropbot/
Project status:
Technical documentation Maturity of the project:
no no
Other
Assembly instructions are editable: Bill of materials is editable: Design files are in original format: No Free redistribution is allowed licence: No
Project management
Open-o-meter: 0 Product category: Business & Industrial Contains original non-electronic hardware: Contains original electronic hardware: Contains original software: |
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Description
DropBot is an open-source Digital Microfluidic (DMF) automation system developed in the . It can be used to manipulate discrete droplets on the surface of an array of electrodes coated with a hydrophobic insulator. DMF has in the fields of biology and chemistry, including diagnostics, cell-based assays, and chemical synthesis. The DropBot features a modular and extensible design, an intuitive user interface, and is capable of driving up to 120 independent channels. It also provides dynamic impedance sensing which enables closed-loop control and real-time measurement of:
- drop position
- instantaneous drop velocity
- electrostatic driving force
System overview
DropBot is built around an -based instrument and is controlled by a custom software interface called . Users can activate/deactivate electrodes on the DMF device by clicking their mouse on the webcam video overlay, providing an intuitive interface with real-time visual feedback. Sequences of actuation steps can be pre-programmed and run automatically, enabling fully automated operation. The system is designed as a loosely-coupled set of modules, which means that it is relatively easy to extend the hardware and/or software capabilities.
Open-source
All components are open-source, subject to the (software code) or (hardware designs), meaning you are free to .
Get involved
If you have any comments or questions, or would like to collaborate on the development of this project, please join the . For announcements concerning future releases/updates, join the or to receive email updates from our ticket tracker, subscribe to the .
Videos
Demonstration of real-time drop control and protocol programming. This video also highlights the systems ability to measure drop velocity from electrical impedance.
Video showing an automated protocol with drop dispensing, merging, mixing and splitting.
Software
Microdrop software
is the graphical user interface for the DropBot DMF automation system.
Control board software
The control board software consists of firmware, a module for communicating over a serial connection, and a plugin for the application.
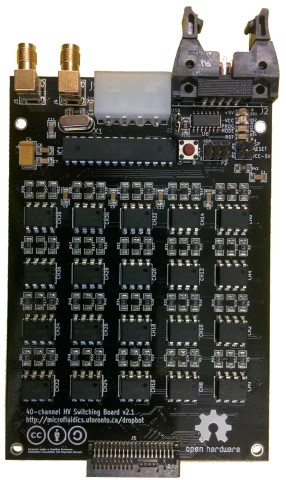
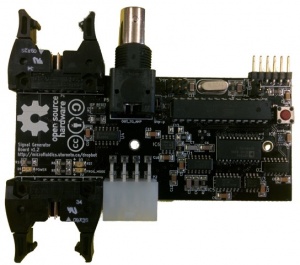
Hardware
All hardware designs can be viewed or edited using or .
Control board
Signal generator board
High-voltage switching board
Pogo pin connector board
Device connector
DropBot case
DropBots in the wild
Here’s a map of all of the (both up and running and those being built). If you are building a system, add a wiki page or link to another webpage/blog to document your progress. Email ryan(dot)fobel(at)utoronto(dot)ca if you want to add a pin to the map.
+ General Reviews 
Public cad repository for non-electronic hardware
Public cad repository for electronic hardware
Public code repository
Assembly instructions
Bill of materials
Contributing guide
Link github